As a South African who’s been in the telecoms market for many years, I’ve witnessed a seismic shift in African economies and the daily lives of its people. This change is spearheaded by the burgeoning access to smartphones, which is unequivocally improving the lives of people across the continent.
I’ve observed firsthand how this increased access is not just a convenience but a catalyst for socio-economic change. We’re now seeing tangible growth in literacy rates, financial inclusion, and economic opportunities that were once a distant dream for many.
In this blog post, I’ll explore the undeniable link between smartphone adoption and economic growth in developing countries, particularly illuminating how digital inclusion paves the way for poverty reduction across the continent.
The Link Between Smartphone Adoption & Economic Growth
With an expected smartphone adoption rate of nearly 87% in sub-Saharan Africa by 2030, we are witnessing a phenomenon reshaping developing countries’ economic landscape.
The correlation between smartphone usage and GDP growth is undeniable.
A recent GSMA Intelligence report on the state of mobile money in Africa revealed that in 2022, mobile technologies helped generate 8.1% of GDP across sub-Saharan Africa, amounting to ~$170 billion of economic value added. This statistic underscores the significant role of smartphone usage in driving development.
Every new user has a ripple effect on the economy, creating jobs, boosting productivity, and stimulating demand in related sectors.
Smartphones are clearly having a profound impact on numerous levels of African society. For example, the spread of 4G/5G technology is impacting banking and commerce, agriculture, education, women’s empowerment, and governance.
1. 4G/5G Technology: Catalyzing Economic Growth
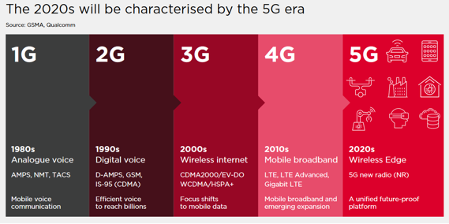
5G technology is now globally accessible, with around 220 operators across more than 80 countries offering these services. Predictions by GSMA suggest that by 2030, there will be upwards of 5.3 billion 5G connections, making up over half of all mobile connections worldwide.
The adoption of 5G in Africa is just beginning, with the region at the early stages of network rollout and commercial use. 4G technology continues to have significant potential for expansion in the region.
However, smartphones remain unaffordable for many, and 60% of the adult population remains offline, despite having access to 3G or 4G signals. As such, the widespread adoption and development of a mature 5G ecosystem is considered a long-term goal for most countries in sub-Saharan Africa.
The significant economic value the mobile industry has generated across the region is impressive, with a direct contribution of $40 billion in economic value in 2021 and support for more than 3.2 million jobs.
In this context, here are some things to keep an eye on:
- 4G leap and 5G exploration: The increasing adoption of 4G networks, soon expected to surpass 2G, alongside early 5G activities, exemplifies the region’s commitment to evolving network technologies that offer expansive career opportunities and foster a more vibrant digital economy.
- Metaverse and connectivity: With mobile operators steering the connectivity needed for emerging digital realms like the metaverse, I see a potential for creative and economic explosion, poised to redefine the digital landscape of African societies.
Mobile operators in Africa are increasing investment in the continent, mostly in expanding 4G networks and this investment is expected to increase as 5G is rolled out.
2. Banking and Commerce
One remarkable area where the impact of internet connectivity and smartphones has been transformative is access to banking and commerce.
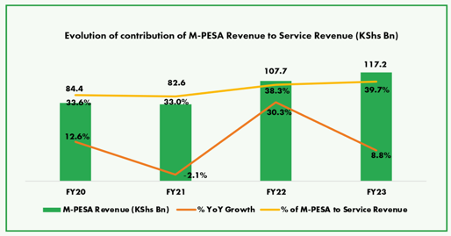
Mobile money platforms like M-PESA have become a staple, allowing over 50 million monthly active users in Kenya to deposit, transfer, and withdraw funds using their mobile phone numbers.
The platform has propelled financial inclusion in Kenya from a low 26.7% in 2006 to an incredible 84% today. In addition to Kenya, M-PESA now operates in seven major African markets: Egypt, Democratic Republic of Congo, Ghana, Mozambique, Tanzania, Lesotho, and most recently, Ethiopia.
Similarly, Airtel Africa reported a 20.4% increase in its mobile money customer base, with Airtel Money reaching 31.5 million users, according to the company’s 2023 investor presentation.
Another example is Zimbabwean mobile money operator EcoCash, which provides services from bill payments to airtime purchases and has increased financial inclusion in Zimbabwe to 88 percent in 2022 with over 10 million users.
According to the Global Findex Database, the number of active mobile money accounts on the continent has grown by 800% between 2012 and 2021, going from 22 million in 2014 to 183 million in 2021.
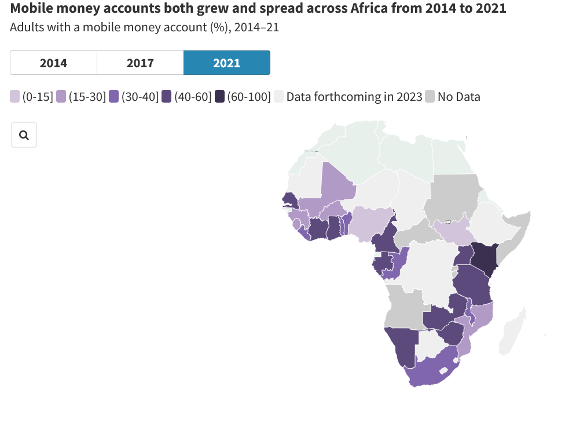
All of these examples have facilitated a surge in financial inclusion and allowed income generation among those previously excluded from formal banking systems.
Agriculture and Food Supply Chains

In the agricultural sector, which plays a significant role in many African economies, access to valuable agricultural information via smartphones has increased agricultural productivity.
Mobile apps like Esoko, a service in Ghana, allow farmers to receive real-time market prices through SMS, increasing profits for those who use the services.
Agricultural advisory services like iCow in Kenya provide farmers with tailored SMS messages offering advice on the gestation period of cows, among other things, reportedly increasing milk production by up to 56% for some farmers.
This streamlining of the agricultural supply chain indicates that developing world economies are on the brink of a farming revolution fueled by digital tools. Furthermore, it showcases the direct correlation between digital access and financial gain.
Education and Digital Literacy

Smartphones provide a fresh and modern gateway to endless knowledge pools, enabling remote learning that overcomes geographical and socio-economic barriers.
E-learning platforms and educational apps are revolutionizing the education sector, catapulting African youth into a future brimming with opportunities. According to a 2024 report by the IMARC Group, Africa’s e-learning market reached $3.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $7.2 billion by 2032.
A Ghanian case study demonstrated that using smartphones for out-of-classroom learning activities, like homework assignments and allowing instructors to send course materials through digital platforms like WhatsApp or email, has improved academic skills for students.
This approach allowed students to bridge the digital divide and access quality educational resources in various formats, including print, audio, and video.
Women’s Empowerment

The embrace of smartphones is fostering women’s empowerment by providing access to healthcare, entrepreneurial platforms, and a voice in areas where they were once unheard. In African societies where women often battle systemic hurdles, smartphones are helping with:
- Enhanced connectivity: Direct access to supportive networks and markets enables women to establish and expand their businesses.
- Information access: Health tips, legal rights information, and educational content all contribute to fostering informed and engaged African women who can better advocate for themselves and their families. The influence of mobile money services must be noticed, too, bringing benefits such as poverty alleviation and easy access to microfinance loans to female entrepreneurs.
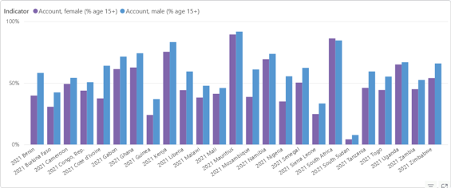
According to data from the Global Findex Database, women in Africa lag in smartphone adoption when compared to men, but that gap is growing smaller in mature markets like Kenya, Uganda, and Ghana. This trend is likely to spread across the continent as new markets become mature.
These changes, driven by the swell of digital inclusion, are slicing through the obstructions of poverty reduction, creating a positive ripple effect that ushers in economic advances across African communities.
Governance and Civic Participation

The ripple effect is tangibly felt as citizens become more politically active and community-oriented, thanks to digital tools that facilitate:
- Community organization: With increased access, citizen groups can more effectively coordinate, share resources, and mobilize for local causes, leading to a participatory democracy.
- Transparent governance: Information flows freely through social media and dedicated apps, holding leaders accountable and ensuring a more open and transparent government process.
Smartphones are changing how people in Africa take part in government and make their voices heard. These devices help people stay informed and encourage them to vote.
For example, easy access to information helps citizens know more about their leaders and government actions. This leads to better awareness and more people participating in elections. In South Africa, for instance, a study found that penetration of 3G mobile internet between 2006 and 2016 helped to increase voter turnout.
Smartphones also let people talk directly to government officials through social media and other apps. This makes it easier for people to share their opinions and for governments to listen.
Health and Quality of Life Enhancements

Beyond the economic benefits, increased access to smartphones improves lives for Africans by fostering a stronger sense of social inclusion and enhancing the quality of life across society.
The improved access to healthcare that smartphones provide is groundbreaking. Mobile health initiatives are transforming patient experiences by offering remote consultations and medical advice without the constraints of distance or the availability of healthcare professionals: •
Health apps: Platforms like HelloDoctor bridge the healthcare divide, offering users immediate medical guidance—a leap forward in Africa’s healthcare paradigm.
Efficiency in treatment: Innovative apps such as Peek Vision and Vula Mobile empower healthcare professionals to diagnose and manage conditions with incredible speed and accuracy, offering patients a new lease on life.
Smartphones are are impacting healthcare in Africa by providing access to medical information, enabling remote consultations, and facilitating disease tracking.
This technology allows individuals in remote or underserved areas to connect with healthcare professionals, receive diagnoses, and manage chronic conditions without the need for physical travel.
Moreover, health apps and platforms are empowering people with knowledge about prevention and treatment, contributing to improved health outcomes across the continent.
Challenges for Smartphone Expansion in Africa

There’s no doubt that increased access to smartphones improves the lives of Africans and is sparking significant strides in social and economic growth.
However, behind this growth lies some challenges, and the industry needs to recognize those that lie ahead in smartphone expansion.
High Cost of Devices and Data
Perhaps the biggest challenge is the cost of devices, as well as data. For many African communities, smartphones are prohibitively expensive, and it doesn’t help that in many countries in the region, taxes and levies increase the prices of new devices by 10 to 30%.
The high cost of data presents another barrier, curtailing access to impactful internet services and reinforcing a cycle that hinders progress. Additionally, currency devaluation, increased taxes, and policy changes to local production, could all drive prices even higher in coming years.
These monetary obstacles risk stifling the economic opportunities smartphones can yield for low-income consumers and hinder the goal of broadened digital inclusion.
The good news is that these challenges, at least in terms of the cost of devices, are opening doors to many opportunities. The advancements of manufacturers like Transsion, and the growth of Chinese brands like Xiaomi, illustrate the demand for smartphone access that can cater to African consumers’ specific needs and economic realities.
Poor Infrastructure and 4G/5G Penetration
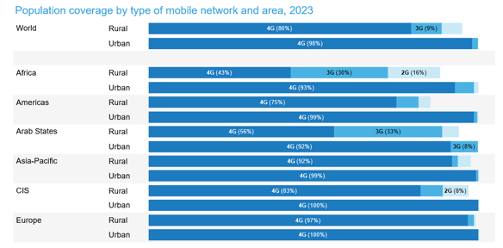
Africa’s tech growth is hindered by weak infrastructure and scant 4G and 5G networks. These hurdles limit smartphones’ impact, stalling progress in key areas like education and healthcare.
While 2G and 3G networks are being phased out in developed countries, they remain a core part of the telecommunications landscape in many African countries. This is because they offer a lower-cost option for providing basic mobile services, such as voice calls and text messages.
Efforts to phase out 2G and 3G are underway, but it’s a slow process. In South Africa, for example, 2G and 3G networks are scheduled to get axed by the end of 2027.
This is a trend that should spread to other countries in the continent, but it might take at least another decade—and even that might be a generous estimate.
According to the International Telecommunications Union, Africa as a whole has the lowest 5G coverage in the world at only 6% as of December 2023.
The next stage of digital evolution in Africa hinges on overcoming these infrastructural challenges to pave the way for a more connected and empowered future.
The Bottom Line
Growing access to smartphones is a powerful force reshaping the lives and economies across Africa.
While challenges, such as affordability, exist, the dedication to overcoming these obstacles paves the way for a more connected and prosperous future.

